The first thing you need to determine is the amount of calories your body needs each day. You could do this a couple of ways. Use the Harris Benedict equation and enter your age, height, & weight; it’ll figure it out for you!
The Harris Benedict equation will help you:
Women: 655 + (4.35 x weight in pounds) + (4.7 x height in inches) – (4.7 x age in years)
Take your number and multiply it based on the information below:
|
Exercise Factor |
Category |
Explanation |
|
1.2 |
Sedentary |
Little or no exercise |
|
1.375 |
Lightly Active |
Light Exercise (1 to 3 days/week) |
|
1.55 |
Moderately Active |
Moderate Exercise (3 to 5 days/week) |
|
1.7 |
Very Active |
Hard Exercise (6 to 7 days/week) |
|
1.9 |
Extremely Active |
Hard daily exercise and/or a physical job |
*This number shows you how many calories you need to consume in order to maintain your weight. As a volleyball player, you would want to multiply by 1.7 (Very active).
Ex. A 20 year old volleyball player who is 5′ 9″ and 154 pounds would need to consume 2,644 calories a day to maintain her weight.
STEP 1: 655+(4.35×154)+(4.7x69in)-(4.7×20)= 1,555
STEP 2: 1,555×1.7=2644
It is so important that you take control of your own food choices when shopping at the grocery store and when eating out. Below I have included some information on how to read a nutrition food label and some general tips.
Reading food nutrition labels:
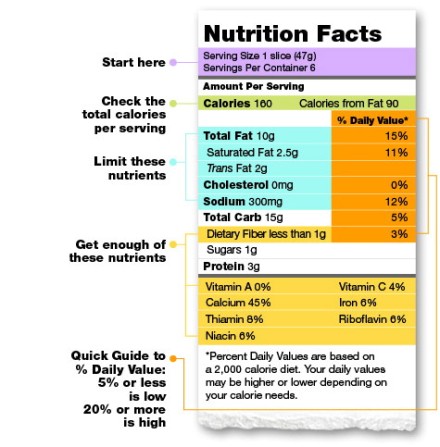
Nutrfacts
Begin by checking the serving size & how many servings per package
- Check the total calories per serving.
- Based on a 2,000 calorie diet: limit total fat to 56-78 g/day
- ≤16 g saturated fat
- ˂2 g trans fat
- ˂300 mg cholesterol
- Make sure you get 100% fiber, vitamins & minerals
- %DV lets you know the % of each nutrient in a single serving, as it relates to the recommended amount of 2,000 calories.
- Want to consume less of a nutrient (fat, cholesterol, or sodium) choose foods with a lower %DV—≤5% is low
- Want to consume more of a nutrient (fiber) choose foods with a higher %DV–≥20% is high
In general:
- 40 calories per serving is low
- 100 calories per serving is moderate
- ≥400 calories per serving is high
- If the panel says “0g trans fat” but includes “partially hydrogenated oil” in the ingredient list, it means the food contains trans fat, but less than 0.5 g per serving
- If you eat more than one serving, you have reached your limit of trans fat for the day
| Fat free | ˂0.5 g of fat |
| Low fat | ≤3 g fat |
| Reduced fat/less fat | 25% less fat than regular product |
| Low in saturated fat | ≤1 g, no more 15% |
| Lean | ˂10 g fat, 4.5 g sat fat & 95mg chol |
| Extra lean | ˂5 g fat, 2 g sat fat & 95mg chol |
| Light | 1/3 fewer calories½ fat of regular product½ sodium of regular product |
| Cholesterol free | Less 2 mg chol & ≤2 g sat fat |
| Low cholesterol | ≤20 mg chol & ≤2 g sat fat |
| Reduced cholesterol | 25% less chol & ≤2 g sat fat than regular product |
| Sodium free/no sodium | ˂5 mg sodium/no sodium chloride |
| Very low sodium | ≤35 mg or less |
| Low sodium | 140 mg or less |
| Reduced/less sodium | 25% less than regular product |
| High fiber | ≥5 g fiber |
| Good source of fiber | 2.5-4.9 g fiber |
*Information comes from American Heart Association 2010
For similar articles, read Nutrition and Supplements