
Volleyball Fitness
Biological Energy Systems
At the cellular level, the high energy molecule ATP provides the energy for muscular contraction and thus human movement.
The replenishment of ATP in muscle is accomplished by 3 basic energy systems:
Phosphagen Energy System
Glycolytic Energy System
Oxidative Energy System
Every sport relies on energy from these 3 energy systems to some degree.
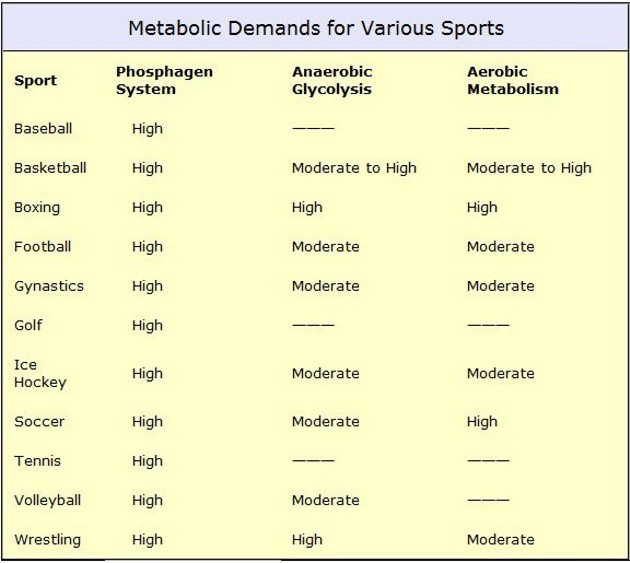
Metabolic demands
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Conditioning
Generally, conditioning can be divided among aerobic and anaerobic training. Training aerobically means using oxygen while training. Training anaerobically means training without using oxygen.
Aerobic exercise generally consists of low-intensity activities performed for longer durations.
Anaerobic exercise generally consists of high-intensity movements performed for shorter durations.
Athletes that train aerobically need a great deal of oxygen to generate the energy needed for prolonged exercise.
Running, swimming, and cycling athletes go a long time with little rest and recovery during their events. These athletes take in large amounts of oxygen during their performance, requiring energy for aerobic sources.
Football, basketball, and volleyball are sports with a shorter duration consisting of high effort and require less oxygen and therefore use anaerobic sources of energy.
The average play in volleyball lasts only 6 seconds and is followed by an average rest period of 14 seconds, not including player substitutions or timeouts (1).
With many breaks during matches, demand for oxygen is much less than many other team sports.
The two primary anaerobic energy sources are the phosphagen system and glycolytic system. While these two energy systems provide most of the energy used in anaerobic activities, aerobic metabolism plays an important role in maintaining power output and energy recovery. (2)
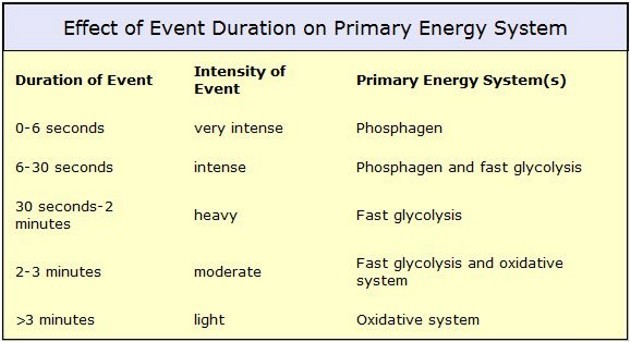
Effect of event duration
How do we train these energy systems?
There are many common methods of training used to increase volleyball fitness. A few are…
Line Drills. Running lines (often called suicides) during volleyball practice is a common method of energy training for volleyball.
Speed Agility Drills. A good strategy may be manipulating the intensity and duration of your speed and agility training. Training can be more time-efficient because you can improve volleyball quickness and multi-directional speed while at the same time train for energy development.
Resistance Circuit Training. Volleyball weight training is anaerobic and should be part of every volleyball player’s training. Weight training trains anaerobic energy systems and can be modified to more specifically target ESD. Simply adjust the work to rest ratios by performing exercises in circuits.
Common resistance used for circuit training include…
Body weight
Free weights
Resistance bands
Sand bags
Kettlebells
Short sprints, agility drills, and circuit weight training that fall into the proper work to rest ratio are most common methods to train energy systems for strength and power sports.
Unlike traditional cardio, your volleyball fitness training should focus on quality of training, not quantity.
Usually there is no need for traditional cardio because Energy System Development can be used to improve the function of the entire cardiovascular system while also developing volleyball fitness.
Volleyball matches are long, but play isn’t continuous. Volleyball fitness training should consist of energy system development specific to increasing or more importantly maintaining a high level of volleyball performance.
For more fun news click here.
Check out the news from our Streching section, every Saturday a new story! Tomorrow read about Static Flexibility Training for Volleyball